Get to know graphene
Graphene is a single-atom-thick film composed of carbon atoms. It has high strength, excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, and is known as the star of future materials.
By Market America WebCenters
•
July 1, 2024
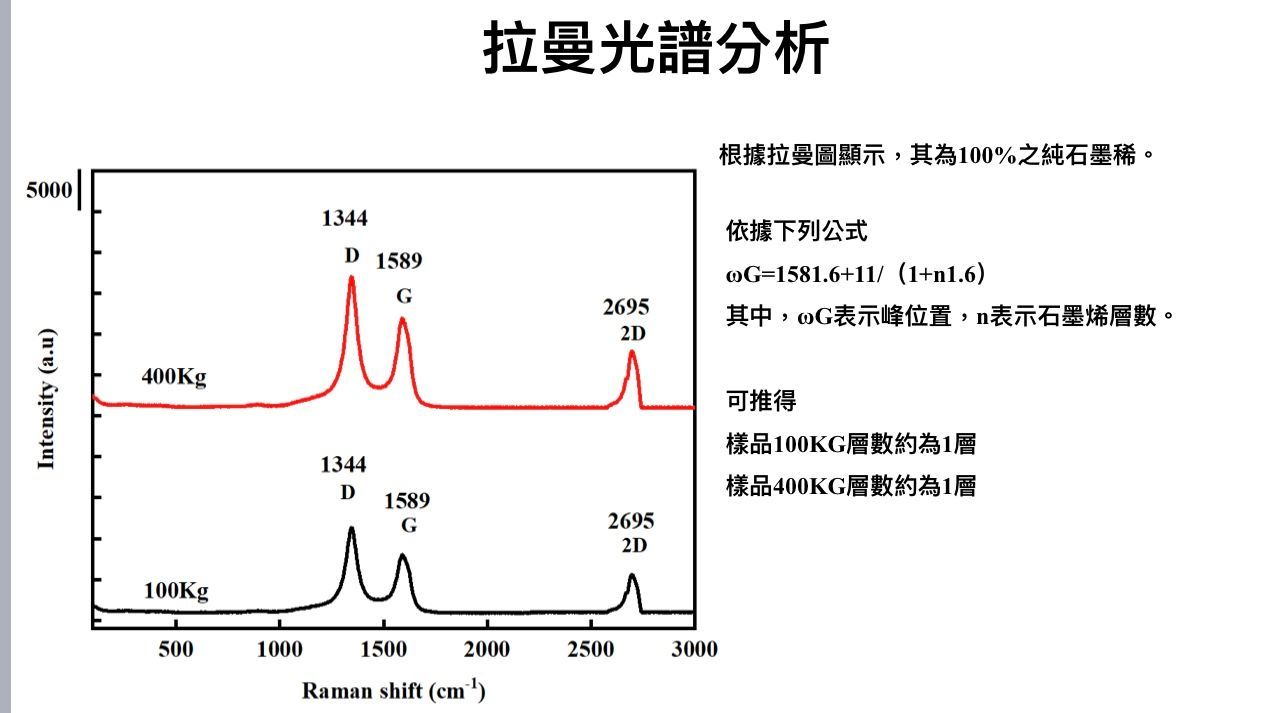
Raman spectroscopy is a very important and powerful optical spectroscopy technique that can provide structural and compositional information of materials. The Raman effect refers to the change in the frequency of photons when photons interact with matter. This change can provide information on the structure and vibration of matter. In Raman spectroscopy, a laser beam shines onto the sample surface, and these photons interact with the molecules of the sample. The frequency of some photons increases or decreases, a change called Raman scattering. By detecting and recording the frequency and intensity of scattered light, scientists can gain valuable information about a sample's structure, chemical composition and lattice vibrations. Raman spectroscopy technology is widely used in various fields, including materials science, chemical analysis, biomedicine, environmental monitoring, etc. It can be used to identify substances, detect trace components, study lattice vibrations, surface adsorption and chemical reaction processes. The high sensitivity and non-destructive measurement properties of Raman spectroscopy instruments make it one of the indispensable tools in modern scientific research and industrial applications. Overall, Raman spectroscopy plays an important role in the field of materials analysis and characterization, providing scientists and engineers with rich structural information to help them understand and apply various types of materials. This is a brief description of the Raman spectroscopy technique, emphasizing its principles, applications, and importance. If you have more specific questions or need to delve further, please feel free to ask.
Address
5F-2, No. 67, Dingxin Road, Sanmin District, Kaohsiung City
Telephone

© Copyright 2024 All Rights Reserved 齊飛管理顧問 製作



